A wire transfer, in a nutshell, is a simple and secure way of sending money electronically from one bank account to another. No cash and cheques move around. No physical handover or associated stress. Just clear instructions passed between banks to shift funds safely.
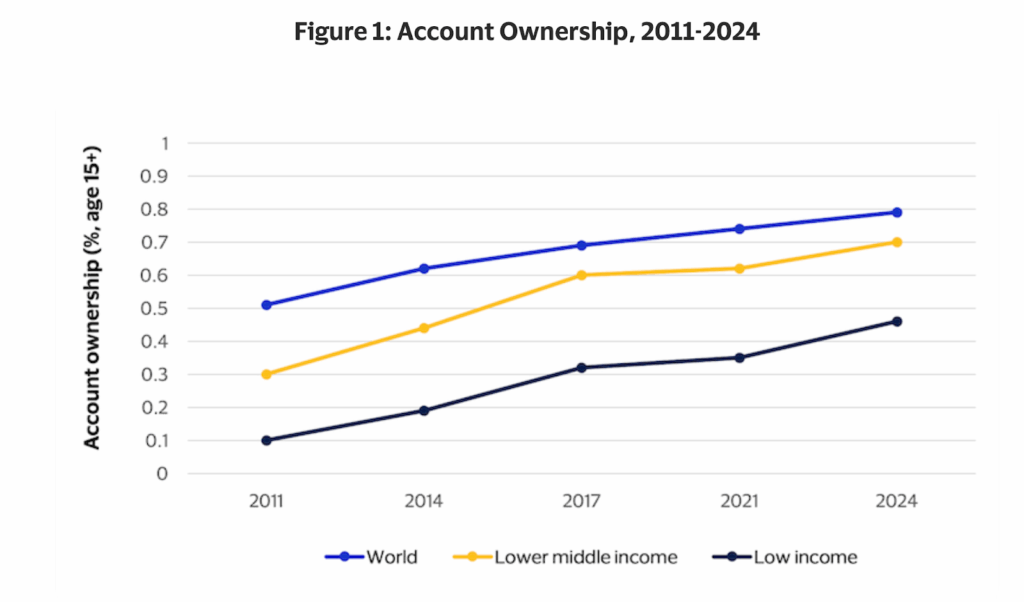
People still rely on wire transfers today, yes, even in a world full of flashy apps because they’re fast, reliable, and work across the globe. According to the World Bank’s Global Findex Database 2025, 79% of adults worldwide now have an account at a bank, financial institution, or mobile‑money provider, showing just how widespread digital banking has become.
Someone in Germany is sending money to their family in Spain. A business in France paying a supplier in India. It happens every single day, quietly and smoothly.
In Europe, systems like SEPA transfers handle everyday payments, while wire transfers step in when the money has to move farther, faster, or with more certainty. It’s in a different league compared to UPI, NEFT, RTGS, or even remittance apps, which feel easy but sometimes lack the seriousness or global compatibility that big payments demand. Wire transfers are more direct, more formal, and honestly, a bit old-school but in a good way.
But here’s the thing. Before sending money, it’s important to understand the safety, the fees, and the tiny details hiding in between. Some charges appear suddenly. Some delays feel random. Knowing how it all works saves time, money, and a lot of unnecessary stress.
Because when your money is crossing borders, you want clarity not surprises. In this guide, we’ll explain to you in detail what is a wire transfer, how do they work, how safe are they and much more.
What Is a Wire Transfer?
A wire transfer is an electronic method through which money is sent from one bank or financial institution to another. Instead of physically moving cash, banks communicate digitally using secure networks to debit the sender’s account and credit the recipient’s account. This system allows funds to be transferred quickly and with a high level of accuracy.
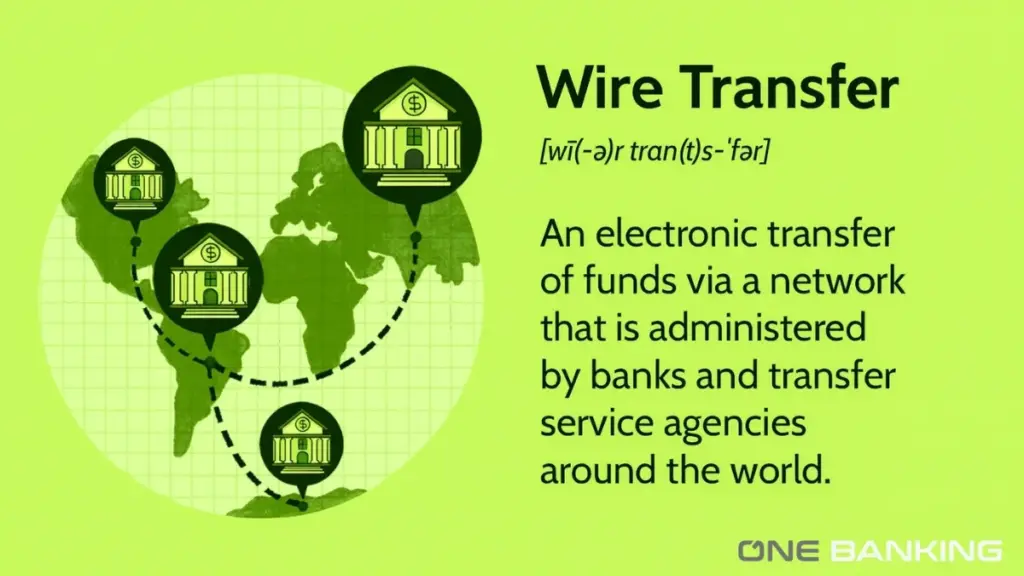
Wire transfers can be carried out domestically, where both banks are within the same country, or internationally, where the transfer crosses national borders. Domestic transfers are usually faster and involve fewer steps, while international transfers may pass through intermediary banks and require additional checks for currency conversion and compliance regulations.
SWIFT payments can be slow and seem costly at some point of time , as they involve several banks working together to pass the payment along – much like synchronizing arrival and departure at a station to get to a final destination.
Because the process is direct, multi- level verified, and supported by regulated banking systems, wire transfers are commonly used for high-value payments, urgent transactions, or overseas financial communication where security and reliability are foremost required.
Types of Wire Transfers
Let’s have a look at the types of wire transfers:
1. Domestic Wire Transfer
A domestic wire transfer is a quick electronic transfer of money between two banks within the same country. It’s straightforward: the sender’s bank debits the account, sends a secure message through the national banking network, and the recipient’s bank credits the funds usually on the same day and can be received within hours because they only need to pass through a domestic Automated Clearing House (ACH). People use domestic wires when they need speed and certainty, especially for crucial or high-value payments
2. International Wire Transfer (also called SWIFT or Telegraphic Transfer)
An international wire transfer moves money across borders using global networks like SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) and is sometimes called a telegraphic transfer (TT).These wire transfers are normally delivered within two to five business days. These extra days are required because international wires must clear a domestic ACH and also its foreign equivalent.
Because banks in different countries must coordinate, the payment may pass through one or more intermediary banks. This can add time, currency conversion steps, and extra fees. Still, despite the complexity, international wire transfers remain one of the most trusted ways to send money safely to someone in another country.
Who Uses Wire Transfers?
Now have a look at users of wire transfers:
1. Individuals Sending Money Overseas:
People use wire transfers when they need to send money to family or friends living in another country. Simple reason — it’s reliable. The money reaches the right person, even if they’re miles away. No confusion. No “app not working” moments. Just a clean, secure and swift transfer that feels reassuring.
2. Businesses Making High-value Payments.
Companies use wire transfers all the time. Big payments. Urgent payments. Payments where mistakes can’t be ignored .
Let’s say , a business in Italy pays a supplier in Japan. A firm in India settling an invoice in Germany. Wire transfers give them that formal, professional pathway. Quick. Traceable. That‘s it!!
3. Institutions Transferring Large Sums Securely
Banks, government bodies, and financial institutions deal with huge amounts. Really huge. And they can’t afford errors or delays. So they trust wire transfers. The process is systematic , documented, and extremely secure. It’s the kind of system where everything is checked twice, sometimes thrice. Because big money needs big caution.
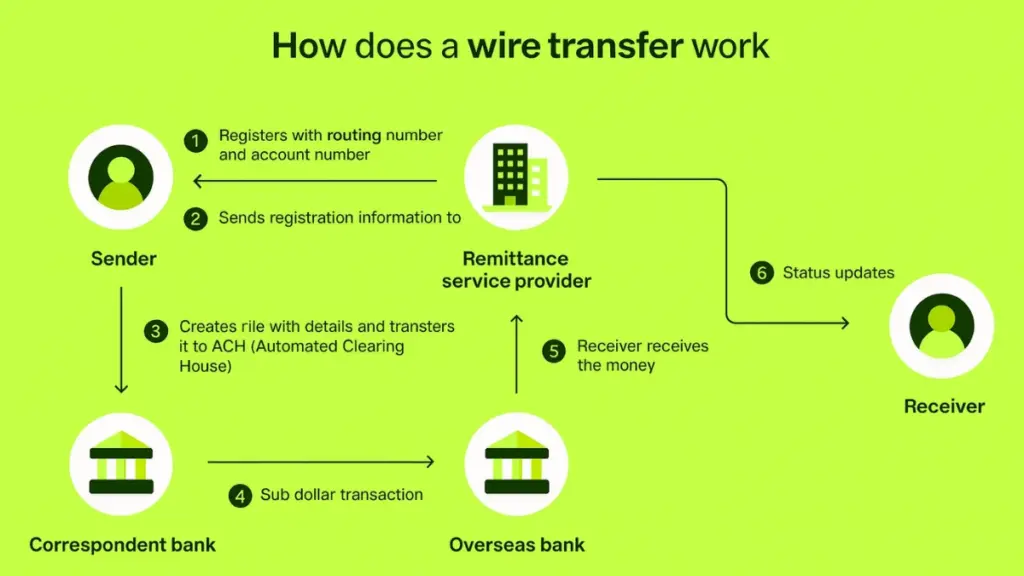
How Does a Wire Transfer Works?
Sender Initiates Transfer: The process begins as soon as the sender provides their bank details, recipient’s name, account number, bank information, and the amount that has to be sent. This is the time when the request officially enters the banking system.
- Bank verifies and processes requests: The sender’s bank verifies everything carefully: account balance, identity, compliance rules, and accuracy of the details. Once satisfied, the bank deducts the amount from the sender’s account and prepares the electronic instructions.
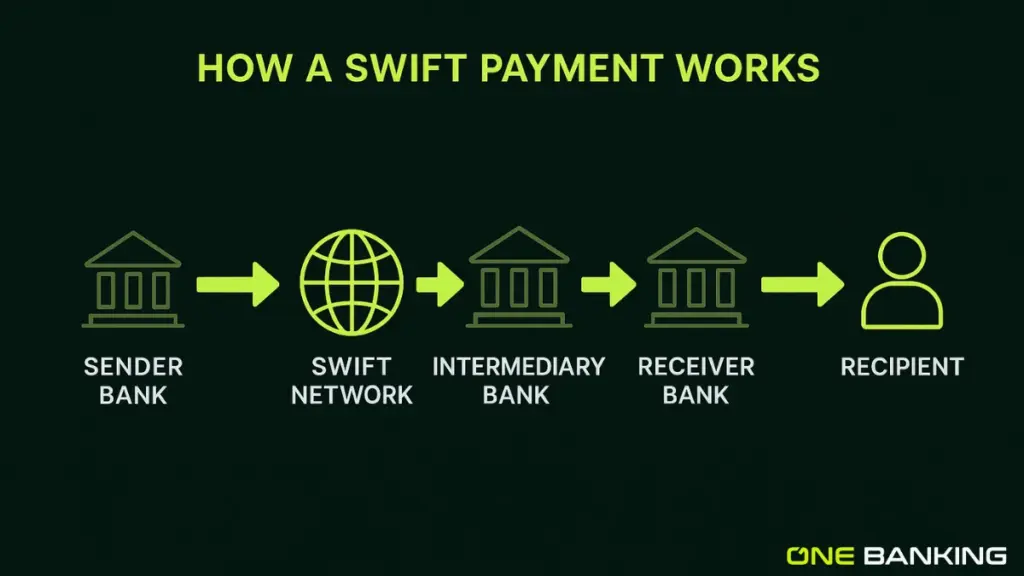
- Intermediary bank (for international) executes SWIFT messaging: For abroad payments, the sender’s bank may not necessarily be directly connected to the recipient’s bank. In that case, an intermediary also called a correspondent bank steps in. It forwards the payment information using the secure SWIFT messaging network. This step ensures the instructions travel safely across countries and currencies.
- Recipient bank receives funds: Just after the SWIFT message reaches the final bank, the recipient’s bank reviews the instructions properly , performs its own checks, and gets ready to label the given amount to the correct account.
- Final deposit into recipient’s account: Once everything matches and no security red flags appear, the recipient’s bank credits the amount to the beneficiary’s account. The funds are now available to the recipient, completing the transfer.
Systems and Protocols Involved
Take a look at the systems and protocols involved:
- Domestic:
Within a country, wire transfers move through regulated payment networks that ensure speed and accuracy, both at the same time .
In Europe, the SEPA system enables fast, low-cost transfers in euros across participating countries, functioning almost like domestic transfers within the region.
In the United States, systems like Fedwire and CHIPS handle high-value and time-sensitive transfers between banks. In India, NEFT and RTGS are widely used NEFT for regular electronic payments throughout the day and RTGS for large-value, real-time transfers.
Each system has its own rules and settlement timings, but all share the goal of moving money safely within national or regional boundaries.
- International:
For overseas transfers , banks usually rely on the SWIFT network, which doesn’t move money directly but sends secure, standardized messages between banks worldwide. These messages carry the payment instructions that guide the transfer from one country to another. When two banks do not have a direct relationship, correspondent banks act as intermediaries routing the payment, handling currency conversion if needed, and ensuring the funds reach the correct final institution. This multilayered structure keeps international transfers secure and connected across global banking .
Required Information for a Wire Transfer
You’ll often be able to set up your wire transfer via your online banking system – although some banks may still require you to visit in person and hand over details in a branch.
Usually, the information needed is quite similar, regardless of who you bank with.
Depending on where you’re sending money to, you might also need to provide additional details such as the source of funds or reason for payment, to comply with the laws in your destination country.
Here, compiling all the stuff needs to be ready beforehand …….
For Domestic Wire Transfer :
- Sender’s details
- Recipient’s name and account number
- Bank name & branch
- Routing numbers / IFSC (country specific)
- Purpose of remittance (for some countries
For International Wire Transfers:
- Sender’s Details
- Recipient account number
- SWIFT code
Types of Wire Transfers: A Deep Dive
Let’s have a look at the types of wire transfers:
1. Bank-to-Bank Wire Transfer
- This is the most traditional and widely used form of wire transfer. Money moves directly from one bank account to another through secure and well systemized banking networks
- Since the process is handled entirely by banks itself, it offers high reliability, strong security, and formal documentation. The fees are usually moderately higher than basic electronic transfers but there it is justified by the speed and certainty it provides. Bank-to-bank wires are typically used for important payments such as property purchases, business settlements and expansions , or international remittances.
2. Online / App-Based Wire Transfers
- Online or app-based wire transfers allow users to send money directly through a bank’s digital platform or a fintech app instead of visiting a branch. It feels simple , open the app, enter the recipient’s details, confirm the amount, and the transfer request is on its way. This digital approach has made wire transfers far more accessible, especially for people who prefer quick, self-service banking.
Advantages:
- Convenience: Everything can be done from home or on the go. No waiting in queues for hours . No hustle.
- Speed: Requests are processed faster because the details are verified instantly.
- Transparency: Apps often show fees, timelines, and exchange rates upfront.
- Accessibility: Fintech platforms make international wires easier for younger or tech-savvy users.
Limitations:
- Transfer limits: Banks and apps may restrict how much you can send in a single transaction or per day, bank fees make wires impractical for some amounts .
- Verification requirements: Big amounts or certain countries may still require in-person checks for security or compliance.
- Not universal: Some routes, especially complex international ones, may not be supported online.
- Technical dependency: Requires stable internet and trust in digital systems something not everyone is comfortable with.
3. Cash Wire Transfers (Western Union, MoneyGram)
- Cash wire transfer is a service designed specifically for those people without traditional bank accounts , here the recipient is supposed to pick up the payment from a nearby agent location as soon as the sender paid it, so we can say it is an instant process .
- Let’s say you are in a shopping mall, asking for money from your friend then what you have to do is to find a nearby agent location using online tools like western union or money gram , will receive payment as soon as you friend sends it.
- Higher fees, instant delivery– just because the convenience and speed are perks of this service, it generally costs higher than normal , more likely depending on the amount that has been transferred .
4. Telegraphic Transfer (TT)
- TT is none other than a common term used to define international wire transfer . It is an electronic method of sending money between banks both locally and internationally . The term originated from a word ‘ TELEGRAPH’ which was an ancient method of sending money . It is a safe and secure method which bypasses frauds since the process includes a lot of intermediary banks and several levels of verifications. This term is more popular in several Asian countries including India.
Domestic vs International Wire Transfers
| Category | Domestic Wire Transfer (DWT) | International Wire Transfer (IWT) |
|---|---|---|
| Processing time | Speed of DOMESTIC WIRE TRANSFER (DWT) is faster, cleared within same day | INTERNATIONAL WIRE TRANSFER (IWT) takes relatively long time, generally 5–6 business days |
| Fees | DOMESTIC WIRE TRANSFER (DWT) generally cost lower with average fees around 30 USD | INTERNATIONAL WIRE TRANSFER (IWT) costs much higher due to potential currency conversion and involvement of intermediary banks |
| Regulations | DWT is under the control of single country rules and regulations | IWT must ensure that it follows rules and regulations of both sender and recipient’s country |
| Systems used | DWT make use of National payment systems, such as Fedwire and CHIPS in the U.S., or TARGET2 in the Eurozone | IWT makes use of The SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) messaging network |
| Cost Comparison | DWT generally costs low to moderate as it is more likely to be a direct transfer within the same country with less involvement | IWT is pretty much costly as it involves multiple level intermediaries |
| Security Differences | DWT are considered more safe as they operate in one single regulatory environment within the same country, typically involved sender and recipient banks | Whereas it is not the case with IWT, it has multiple level risk factors due to complexity of this system with the involvement of several intermediaries and different regulatory environments, hence the chances of fraud cases in IWT increases manifolds |
When to Use Which?
Now when it comes to what to choose while making payments is more importantly depends on various factors such as destination, urgency and nature of transfer
- Whenever we have to make transactions locally , within our country , we are supposed to go for domestic wire transfer, be it your real estate payments or some kind of urgent payments .
- Since domestic wire transfer is cleared within the same business day with a clear record of transaction, it makes it more preferred for large transactions and same country payments.
- We will opt for International wire transfer for our overseas payments, be it sending money to your child for educational purpose or making payments for business enthusiast
So next time, whenever you are sending money from India to Europe as a part of family remittance , you as of now understand that you are using international wire transfer.
How Long Does a Wire Transfer Take?
Have a look at how long does a wire transfer take:
- Domestic Wire Timelines: When we have come down to this point after reading so long , we have very well understood that domestic wire transfers are very instant payments with more likely to get cleared in a few hours or same business day due to very simple procedures .
- International Wire Timelines: Since we know it is a very complex procedure, with involvement of several levels of verification and a large number of details it requires , it approximately requires 4-5 business days for all kinds of verifications .
Factors That Delay Transfers
When sending money over international wire transfer, there are several factors which cause delay in transfer apart from actual payment processing. These are as follows:
- Time Zones: When we opt for transfers between two countries having significant time differences , it causes delay since banks in both countries are working during different local hours .
- Banking Hours: If any transaction is initiated outside of the local business hours of the bank , then such transactions have been delayed till next business day .
- Holiday Schedules: All kinds of national and regional holidays in either country ( senders or receiver) are likely to freeze that payment till the next working day.
- Incorrect Details: This is one of major problem faced with international wire transfer , that any kind of mistake is not entertained at any intermediary level , firstly it requires a huge set of information to make that payment like account number , swift code , recipient name ,and kind of discrepancies in any of these is not entertained and immediately rejected , making it a major reason of delay in overseas payments.
- Intermediary Bank Processing: International transfers route its pathway through intermediaries , which in turn itself requires a reasonable time to process that payment, causing delay with some extra applicable charges.
For many users today, fintech apps like oneBanking offer a digital alternative; providing secure money transfers along with tools to compare fees, track status, and monitor exchange rates in real time.
Wire Transfer Fees Explained?
Wire transfer fees are charges which are part of the overall transaction we are undertaking. Understanding each one of them helps us to understand the overall cost we are paying.
Types of fees:
- Outgoing fees: This fee is charged by your original bank to initiate that payment , the amount varies significantly depending upon whether the payment is made locally or internationally .
- Incoming fees: This fee is charged by the receiver bank, again which varies from bank to bank. Individuals have to check for their bank schedule for this .
- Intermediary/correspondent bank fees: This plays a major role in international wire transfers where all intermediaries who are themselves processing that payment deduct some fee to verify all details and finally make that payment successful.
- Exchange rate markup (hidden fee): transferring funds overseas , requires currency exchange which in turn has some hidden charges to initiate that process of currency conversion, about which all of us can’t do anything directly.
So after adding all of these charges what it results is that the amount that has been sent to another person, deducted over route and recipient receives some less money than what has been sent .
Why Wire Transfers Can Be Expensive?
Wire transfer can be expensive due to involvement of many operational needs , security maintenance, SWIFT charges and cross – border compliances costs.
- High operational security: When it comes to reliability, banks invest heavily to keep security up to date to prevent frauds, to protect large sums of money . The trust of the masses depends heavily on security .
- SWIFT charges: international payment transfer heavily depends over the SWIFT network.This messaging network and all intermediary banks levy fees from the sum that has been initiated by the sender.
- Cross-border compliance costs: All of these financial institutions must adhere to norms of AML (Anti Money Laundering) and KYC (Know Your Customer ) laws. Hence, verification of each transaction requires huge competent team work and management , whose costs also get incorporated in sum amount.
Tips To Reduce Wire Transfer Costs
- Use fintech options (Wise, Revolut): Generally online first services like revolut and wise charges lower fees and provide better exchange rate than traditional banks.
- Avoid weekend transfers: An individual must ensure that he is not making transfers during weekends and regional holidays as it would result in further delay .
- Use correct recipient information: Double check and cross verify all the details before sending as it generates undue chaos and may charge some extra fee.
- Compare exchange rates before sending: Always compare the total cost, including the exchange rate markups, across different services before sending.
- Sending money in recipient’s currency: When we send money in recipient’s currency , it cuts down the extra fees which is charged for currency conversion .
Are Wire Transfers Safe?
Security Features
- Encrypted Banking Networks: For securing data transferred over wire transfer, these financial institutions use advanced encrypted protocols. It ensures that sensitive information like account number , transfer details are transferred privately.
- SWIFT Authentication: Majority of international transfer is facilitated by SWIFT networks. SWIFT utilizes standardized, secure messaging protocols and authentication procedures to verify the identities of the intermediaries involved in a transaction,which in turn add a layer of trust and security to international transfers.
- KYC/AML Checks: Banks are bound to follow KYC (Know Your Customer ) and AML (Anti Money Laundering) regulations. These checks are required to verify the profile of their customer and monitor transactions for safe and secure transfer.
Common Risks
While mostly secure, wire transfers do have some risk associated with it, some of them are as follows;
- Irreversibility: Sending money over wire transfer is like sending cash , once transferred , recovery is almost impossible.This is why , an individual must ensure entering the right recipient bank details.
- Fraud vulnerability: Scammers may try to trick you to make unauthorized transfers . Thus, general lack of security tools make it difficult to recover lost amounts.
- Exchange Rate Risk: International transfers are mediated through currency conversions, exchange rate conversions affect the final amount received.
How To Protect Yourself?
- Verify Recipient Details: Double check for recipient details to avoid related discrepancies.
- Avoid Email-based Instructions: Don’t blindly trust the info sent over mails.
- Confirm with the bank: While sending and receiving money , confirm it with bank
- Use two-factor authentication: Two-factor authentication (2FA) protects you during wire transfers by adding a critical, second layer of identity verification that an attacker would not have, even if they compromised your password.
Red Flags for Wire Transfer Scams

- Urgent Payment Demands: Scammers trap you to make urgent payments by creating need of urgency where you have no time left to think and verify details .
- Unknown Sender Requests: Fraudster mimics being recognised and sends money requests to meet their goals .
- Prize/lottery Winnings: Don’t fall into trap of fraud where they charge extra fees to receive so called lotteries or prize
- Romance scams: Scammers build a fake emotional or romantic relationship online and then ask for money for emergencies, travel, or other fake crises
- Phishing Emails with Changed Bank Details: Scammers hack into email accounts or create convincing fakes and request that you change existing payment details to their own bank account
Regulations and Compliance
Let’s have a look at the regulations and compliance:
1. Domestic Regulations
Depending on the country’s central bank policies: domestic transfers depend heavily on the country’s central bank policies, which defines rules and policies for financial institutions.
2. International Compliance Checks
- AML
- FATF
- Sanctions checks
- LRS (India), OFAC (US), etc.
Limits on Wire Transfers
Wire transfer limits are determined by a combination of country-specific rules and regulations , bank-specific policies, and transaction types.
Wire transfer limits at European banks vary significantly by institution and transfer type (SEPA, international, instant) and are set by the individual bank rather than a single regulatory body
For example, BNP paribas: offers limits Up to €6,000 per day for standard transfers online.
Whereas for international transfers (SWIFT), the maximum limit is around €50,000 per transfer.
In India’s Liberalised Remittances Scheme (LRS) sets a country-wide limit of $250,000 USD per financial year for resident individuals, while individual banks like State Bank of India (SBI) may set their own per-transaction or daily limits, such as $40,000 USD.
Alternatives to Wire Transfers
While wire transfer is one of the most common methods of money transfer , we still can prefer other options which offer advantages in speed and cost. The best choice often depends upon specific needs of sender and receiver like destination country , amount , urgency .
ACH Transfers
- The Automated Clearing House (ACH) network is a U.S. based electronic funds transfer system . It is commonly used for direct deposits and payments within the U.S. only .
- Pros: Generally much cheaper than wire transfers , often they are free for standard transfers.
- Cons: Slower than wire transfers , generally taking 3 to 5 business days.
UPI / Instant Payments
- Several countries have already established their instant payment system with minimal or zero costs to users similar to India’s UPI(Unified Payment Interface).
- Notable examples are India’s UPI, Brazil’s Pix, and the EU’s SEPA Instant Credit Transfer (SCT Inst).
Online Money Transfer Platforms
- There are many online money transferring platforms which offer various services tailored to different needs such as overseas transfer , business payments, cash on receipts.
- Some notable platforms include wise , pay pal, Remitly, western union, money gram, Payoneer, WorldLemit and XE.
Bank Drafts / Cheques
- Bank draft and cheques are some of the traditional payments system which are not as immediate as modern digital options, but generally inexpensive
When Should You Use a Wire Transfer?
Take a look:
Best Use Cases
- High-value payments
- Urgent or time-sensitive transfers
- International education payments
- Overseas property purchases
- Business imports/exports
When Not to Use a Wire Transfer
- Small-value transfers
- Non-urgent transactions
- Cases where cheaper alternatives exist
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Send a Wire Transfer
STEP 1: Prepare Your Information
STEP 2: Verify Bank Details
STEP 3: Initiate via Bank/Online
STEP 4: Track the Transfer
STEP 5: Confirm Receipt
Conclusion
Wire transfers remain a trusted backbone of global banking, especially when you need speed, reliability, traceability, and formality (for large payments, overseas remittances, business / institutional transactions). But as digital finance evolves, many people now also expect convenience, transparency and real-time tracking, and that’s where modern banking apps come in.
If you use a well-designed finance app such as oneBanking, you get the best of both worlds: you retain the safety and formality of traditional bank-wire transfers, while enjoying digital-age conveniences like real-time notifications, easier recipient management, and immediate access to transfer history.
Ultimately, the choice between a classic wire transfer and a digital-first platform depends on your situation. For high-value or cross-border payments, traditional wire may still be best, but for smaller amounts, frequent transfers, or everyday use, a digital banking solution like oneBanking can be faster, easier and often cheaper.
Be aware of hidden fees, exchange-rate markups, and security risks. Always double-check payment details, prefer secure networks, and keep a record of transfers. Doing so ensures your money moves smoothly, whether through wire or via digital banking.
If you use a well-designed finance app such as oneBanking, you get the best of both worlds, the trust of traditional banking and the convenience of modern digital tools.
Key Takeaways
- Knowledge of fees, timelines , exchange rates and associated risks will help in eliminating delays and unnecessary cost and promote safe and secure transfer.
- Awareness kills surprises, about hidden charges, intermediary banks deductions, hold period. Thus, empowered customers take wise decisions.
- As per your need,explore all options , compare banks , apps , fintech platforms and other services and choose accordingly
- Practice responsible transfer habits like cross verifying recipient details,keeping transaction records, using secure networks and choosing legitimate providers.
- With the right knowledge and careful evaluation, wire transfers can be used effectively, efficiently, and safely in a fast evolving global financial environment.
FAQ’s:
A wire transfer is an electronic method of transferring money from one bank to another , without involving in hand cash. It is a fast secure method of sending money both domestically and internationally.
No, wire transfers are not instant , they can take anywhere from a few minutes as in domestic wire transfer to several business days as in international transfers.
To make a wire transfer, you need the recipient’s full name, address, and bank account information, including the bank name, routing number (ABA), and account number. For international transfers, you’ll also need the recipient’s SWIFT/BIC code and potentially an IBAN number.
A wire transfer can cost anywhere from free to over $75, depending on whether it is domestic or international, the financial institution, currency conversion charges and the amount being sent.
A wire transfer is a fast, secure method for sending money, often internationally, that uses networks like SWIFT and involves higher fees, while a bank transfer is a broader term, typically used for slower, domestic transactions through networks like ACH that are usually cheaper or free.
You may be able to cancel a wire transfer, but your chances of success depend on how quickly you act . The best time to cancel is immediately after sending it, especially within the first 30 minutes for international transfers, or before the next business day if you sent it over a weekend or holiday.
Your international wire transfer is likely to be delayed due to security and compliance checks, the number of intermediary banks involved , and processing times across different time zones.
A SWIFT code is a unique Bank Identifier Code( BIC) used to identify specific banks and financial institutions for international money transfers. It is needed for cross-border transactions to ensure that funds are sent to the correct bank and branch.
Yes, generally it happens when scammers encourage you to make fraudulent transfers.
No, wire transfers are generally irreversible once initiated, especially after they have been fully processed and deposited.
ACH transfers are ideal for low-cost, domestic, and recurring payments like payroll, while wire transfers are better for fast, high-value, or international transactions like a real estate closing.
Yes, weekends and holidays significantly affect wire transfer periods because banks and financial institutions do not process them on non-business days. International transfers are even more susceptible to delays due to different holiday schedules in other countries.
An intermediary bank is a third party bank which facilitates international wire transfers , where a sender and recipient do not have direct relationship .
To track a wire transfer, you’ll need the transaction reference or confirmation number provided when the transfer was initiated.
Yes you can , login to your mobile banking app , go to the international wire transfer section and enter details like recipient account number , SWIFT code . Make sure to review the exchange rates and hidden charges before initiating payment.
Daily wire transfer limits vary significantly based on the bank, account type, and whether the transfer is domestic or international, but they are generally higher than other digital transfers.
You typically need to share your bank account number to receive direct bank transfer, as it will help in determining your specific account.
A wire transfer itself is a method of moving money and is not a taxable event. Instead, the taxability depends on the underlying purpose and source of the funds being transferred.
If you enter wrong details in a wire transfer, the transaction may be delayed, rejected, or sent to the wrong account. You should first check if it failed automatically, and if not, contact your bank immediately to report the error and request a reversal.
Yes, a telegraphic transfer (TT) is the same as a wire transfer. The terms are interchangeable, with TT being a legacy term for the same electronic, international bank transfer process used today. Both terms refer to the electronic transfer of funds between banks, most often using the secure SWIFT messaging system to send payment instructions across borders.
A “wire transfer troubleshooter” is a tool or service that helps users diagnose and resolve problems with electronic money transfers, which are also known as wire transfers or Telegraphic Transfers(TT). These problems can include delays, incorrect recipient information, or failed transfers. The troubleshooter can guide users through common issues to ensure the money arrives at the correct destination or to identify what went wrong and how to fix it.