Blockchain banking uses blockchain technology, which is a decentralized and shared digital ledger, to make traditional banking processes like payments, identity verification, and settlements faster and more secure. In 2025, 87% of banks in G20 countries are already using blockchain or distributed ledger technology for tasks such as KYC, clearing, and payment settlements.
The blockchain market in banking and financial services is growing fast: it was valued at $6.98B in 2024 and is projected to reach $10.85 by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 55.3%. This growth is driven largely by use cases in cross-border payments, digital identity, and smart contracts.
As more people shift to digital banking, apps built on modern technology have a clear edge. That’s exactly where the oneBanking App shines. People expect faster payments, strong security, and the convenience of managing everything from one single place. Blockchain technology in banking helps make this possible by reducing fraud risks, speeding up verification, and lowering the cost of international transfers.
In this blog, you will learn about blockchain banking, how it works in simple terms, why banks are adopting it so quickly, and how tools like the oneBanking App fit into this new digital landscape.
What Is Blockchain Banking?
Blockchain banking is a unique type of banking that uses blockchain technology. It includes distributed, decentralised digital ledger for banking processes rather than relying purely on traditional centralised databases. A blockchain ledger records transactions in “blocks” that are time-stamped, linked in a “chain,” and shared across multiple participants. Once a transaction is recorded and verified, it is immutable; it cannot be altered or deleted.
In the context of banking, this opens up new possibilities: banks can share ledgers securely, verify identities more efficiently, automate contracts, and provide customers with clearer visibility into their transactions. By employing blockchain in banking (i.e., Blockchain Banking System), institutions can rethink the traditional architecture of banking services.
Why Banking Needs Blockchain: The Key Drivers?
Let’s explore the major pain points in conventional banking and see how blockchain addresses them.
Inefficiency and Slow Settlement
In traditional banking, especially for cross-border payments or trade finance, multiple intermediaries (correspondent banks, clearing houses, settlement systems) are involved. Each adds time, cost, and complexity. With blockchain technology in banking, transactions can be validated across a peer network and settled much faster, sometimes near-instantaneously.
High Costs and Redundant Processes
Manual reconciliations, legacy system maintenance, paper-based compliance, and middle-man fees all add up. Blockchain banking can streamline workflows through automation (smart contracts) and reduce the need for intermediaries, thereby lowering costs.
Lack of Transparency & Traceability
When a transaction moves through multiple systems, visibility is limited. Customers and banks alike may not know status, risk of errors, or fraud is higher. In blockchain banking, ledgers are cryptographically secured and immutable, creating a clear audit trail.
Identity & KYC Friction
Banks often spend huge effort and cost in Know-Your-Customer (KYC) processes, yet still face identity fraud or duplication. Using blockchain technology for identity verification provides a single, shared, verified digital identity that multiple banks can trust, reducing duplication and risk.
Given these pressures, many banks and financial institutions are exploring how Blockchain Technology in Banking can be a meaningful upgrade to their systems.
How Does Blockchain Work in Banking?
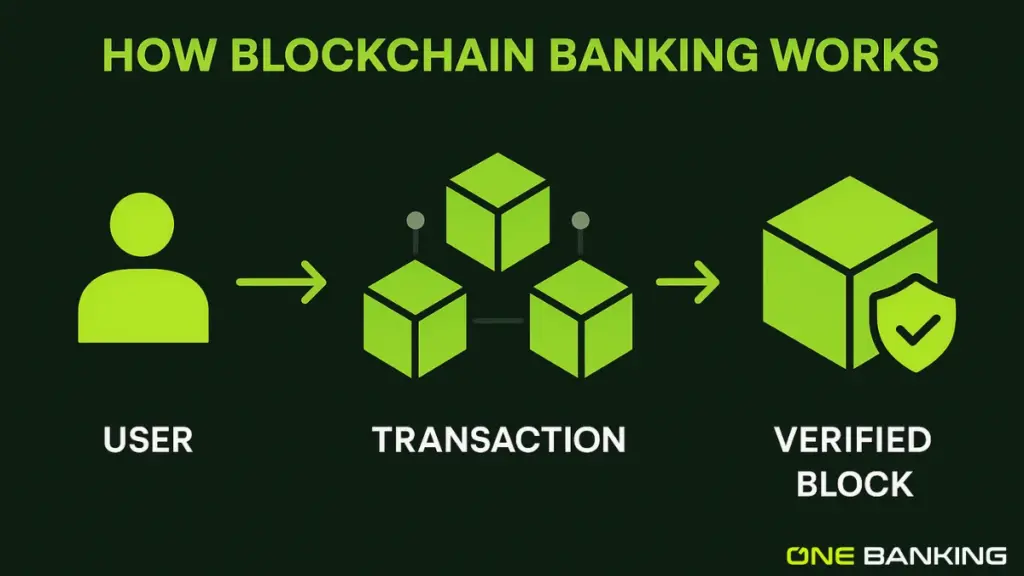
Let’s break it down into simpler terms.
- Distributed Ledger: Instead of one bank’s database, many nodes (computers) across the network each hold a copy of the ledger.
- Blocks & Chain: Each transaction becomes a “block” that is verified by the network, time-stamped, locked in, and then added to the “chain.” That chain cannot be changed without the consensus of the network.
- Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts with terms written into code. For example, once certain payment conditions are met, the contract automatically executes.
- Permissioned vs Public Blockchains: In banking, typically permissioned (i.e., private or semi-private) blockchains are used: only authorised participants (banks, institutions) can join, which helps maintain privacy and compliance.
- Immutable Audit Trail: Every transaction is traceable and cannot be tampered with, which means better auditability.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain in Banking
Blockchain is already being used by banks in practical ways. These are the areas where it makes the biggest impact.
1. Cross-Border Payments
Cross-Border Payments is one of the strongest use cases. Traditional international transfers often move through several banks and can take two to five days. With blockchain technology in banking, the transfer is recorded on a shared network and can be settled in a few minutes. This reduces delays, lowers fees, and gives both the sender and receiver a clear view of the transaction at every step.
2. Trade Finance
Trade finance deals with many parties. Exporters, importers, banks, insurers, and shipping companies all need to review documents and verify details. This process is usually slow and paper-heavy. Blockchain creates a single shared ledger where each party can see updated information in real time. This reduces the risk of fake documents, speeds up approvals, and improves trust between everyone involved.
3. Identity Verification and KYC
Know Your Customer (KYC) checks are required by law, but they are often repeated every time a customer applies for a new financial product. With blockchain, a customer can have a secure digital identity that is stored on the network. Once verified by one bank, the same identity can be shared with others. This cuts down on repeated checks, reduces cost, and makes onboarding faster and safer.
4. Smart Contracts for Loans and Syndicated Lending
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements stored on a blockchain. They trigger actions automatically when all required conditions are met. For loans, this means that once collateral is approved and credit checks are completed, the money can be released without manual steps. This reduces paperwork, removes delays, and lowers the chances of human error.
5. Asset Tokenisation
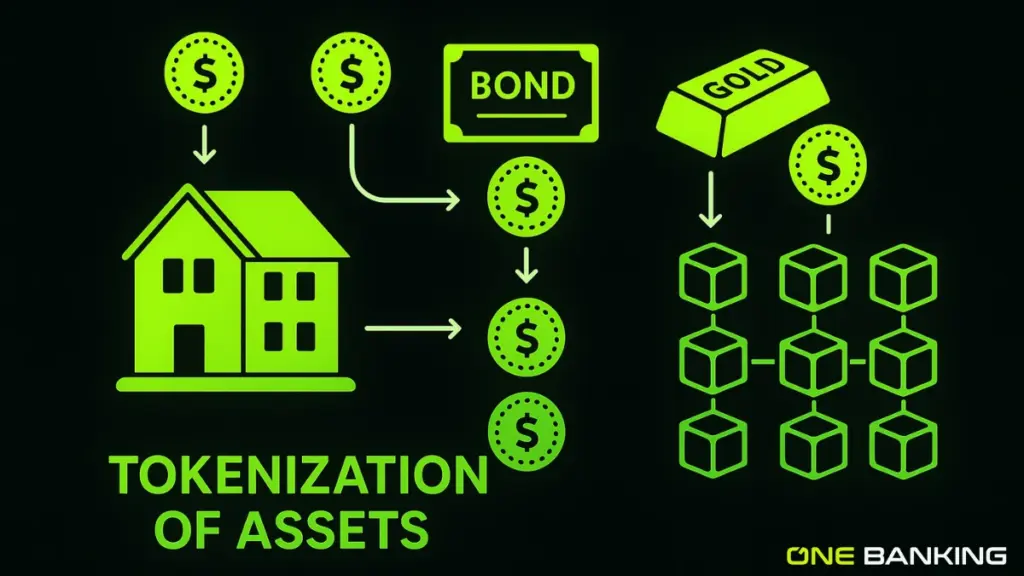
Real-world assets such as real estate, bonds, or gold can be turned into digital tokens on a blockchain. Each token represents a piece of the asset. This makes it possible to own small fractions of high-value assets, trade them more easily, and improve liquidity. It also opens the market to more people who could never invest in these assets before.
Which Banks/Institutions Are Using Blockchain Technology?
Some major global banks and consortia have already launched initiatives involving blockchain:
- JPMorgan Chase has created a private blockchain network for wholesale payments.
- HSBC and others are exploring trade-finance ledgers built on blockchain technology.
- UBS Group, Barclays, and other banks have joined consortia focused on cross-border settlement using blockchain.
The Challenges & What Still Needs to Be Solved
While the promise is strong, there are still practical hurdles.
1. Scalability
Blockchain systems often face a “trilemma”: you can optimize for decentralisation, security, or scalability, but not all at once. High transaction volumes (as seen in banking) demand speed and efficiency, which many networks struggle with.
2. Legacy System Integration
Banks have decades of established infrastructure; migrating or integrating to blockchain platforms is costly and complex.
3. Regulatory and Compliance Uncertainty
Different countries have different laws around blockchain, digital assets, and data protection. Banks must navigate this carefully to avoid risk.
4. Privacy vs Transparency
Blockchain is transparent by nature; banks and customers often require confidentiality. Finding the right balance between visibility and privacy (especially for regulated banking) is still a work in progress.
5. Energy Consumption & Network Costs
Some blockchain models (especially older ones) require significant computing power. For banking, scale, cost, and sustainability matter.
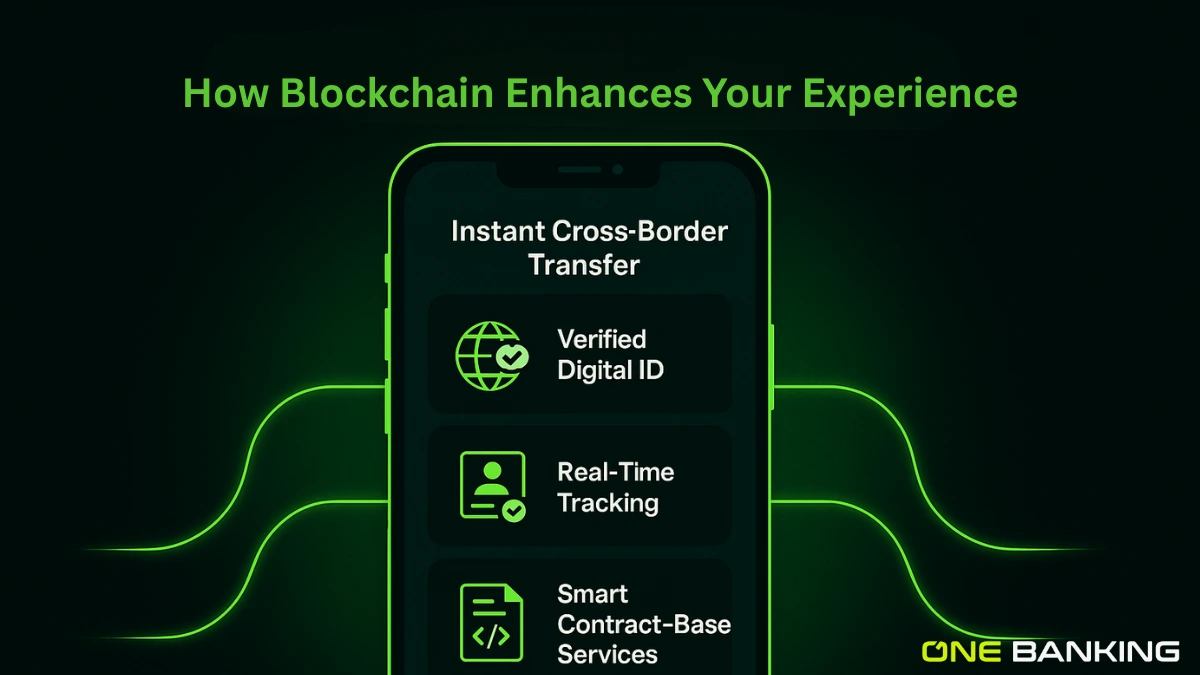
How oneBanking App Uses Blockchain to Upgrade Your Banking Experience?
At oneBanking App, our goal is to bring blockchain-powered banking closer to you without the complexity. Here’s how:
- Instant cross-border transfers: By partnering with blockchain-enabled networks, we reduce transfer times and transaction fees, making international payments smoother.
- Transparent transaction tracking: You’ll be able to see status updates more clearly, where once you were always “waiting,” you’ll now know the movement of your funds.
- Secure identity and verification: We’re exploring digital identity frameworks using blockchain to streamline onboarding and reduce repeated KYC steps.
- Automated contract-based services: Imagine a loan or investment product that triggers automatically when conditions are met, with fewer manual steps, less waiting.
- Better accessibility: Whether you’re a business doing trade finance or an individual transferring money globally, the same backbone technology gives you more inclusive access.
The Future of Blockchain in Banking
Let’s look ahead to what’s coming next.
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Many central banks are exploring or piloting digital currencies issued on blockchain. This could change how commercial banks and customers interact with money.
- DeFi (Decentralised Finance) + Banking Hybrid Models: Peer-to-peer lending, “programmable money”, tokenised assets, all potentially merging with traditional banking to give you new kinds of financial services.
- Real-time settlement everywhere: Not just cross-border payments, but stock trades, loans, insurance claims, and more may become near instantly settled thanks to blockchain.
- Enhanced regulatory technology (RegTech) and compliance built in: Blockchain’s audit trail and transparency mean regulatory compliance can be more automated, less manual, good for banks, better for you.
- Inter-blockchain interoperability: As more networks develop, banks and apps like oneBanking App will connect across chains, systems, and geographies, making banking seamless across borders and systems.
Conclusion
The world of finance is shifting, and the banking experience you’ve known—slow transfers, heavy fees, opaque processes is being challenged. With blockchain banking, your future could hold a set of services that is transparent, fast, and low-cost.
We at oneBanking App welcome this transformation. We’re building on the premise that blockchain isn’t the silver bullet, but with the right approach, it can revolutionise banking.
Whether you are transferring cash across borders, making an investment, or simply doing your day-to-day banking, understanding and embracing blockchain banking, its technology in Banking, and blockchain Banking Systems will put you ahead of the curve.
When you’re ready for better banking, faster, simpler, smarter, the oneBanking App is here for you.
FAQs
1. What is Blockchain Banking, and what does it offer banking?
Blockchain Banking uses blockchain technology to record and verify financial transactions in a distributed, immutable manner. It offers faster settlement, greater transparency, lower costs, and more efficient compliance.
2. Will blockchain replace banking?
Not entirely. Instead of doing away with banks, blockchain will reshape how banks operate, shifting them from central ledger‐keepers to network participants and trust anchors.
3. Which bank is using blockchain?
Global institutions such as JPMorgan Chase, HSBC, Barclays, UBS, and others have launched blockchain initiatives for payments, trade finance, and settlement.
4. What does blockchain offer banking?
Blockchain gives banking enhanced security (immutable ledger), improved transparency (shared transaction record), lower costs (fewer intermediaries), faster processes (near-instant settlement), and new product potential (smart contracts, tokenised assets).




Wilfried Streiner
Very interesting topic, it is excellently demonstrated how important blockchain technology really is in the financial sector.
oneBanking
Thank you, please share with other too.