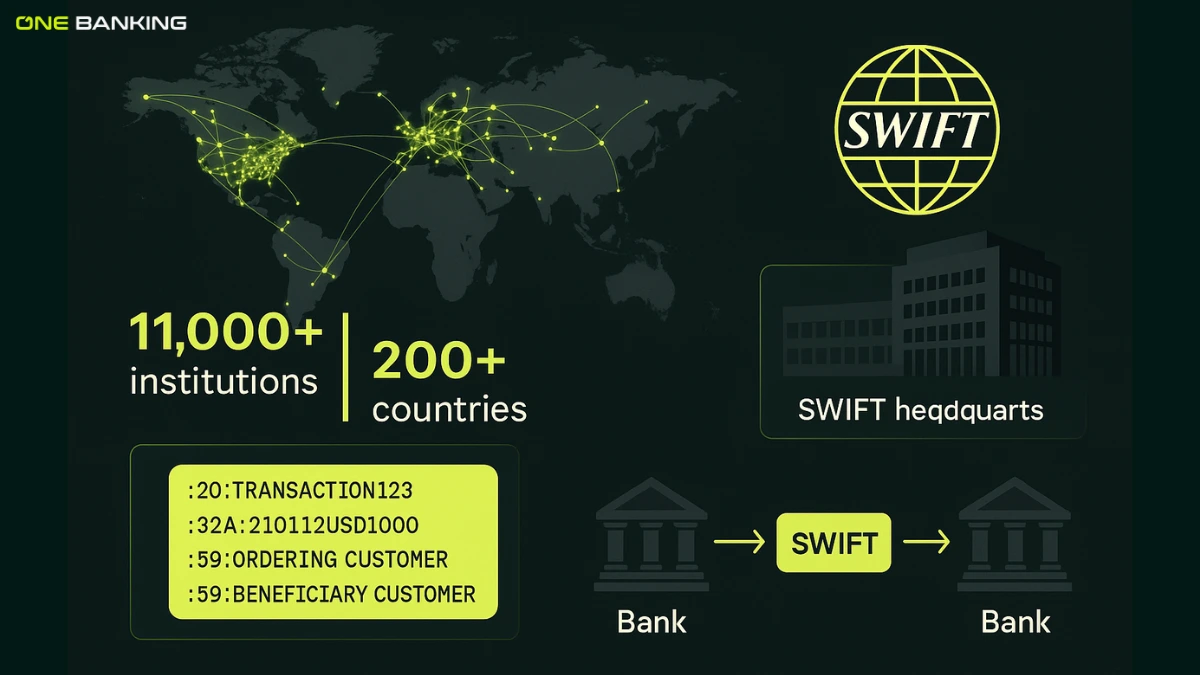
When we talk about international payments, the same two terms appear everywhere: SWIFT Code and Blockchain. Even though blockchain-based networks can process transactions in seconds, more than 11,000+ banks and financial institutions across over 200 countries still rely on the SWIFT network for cross-border communication. In fact, nearly $150 trillion is routed annually using SWIFT messaging.
So the question is simple: If blockchain is faster, why aren’t banks shifting to it completely?
In this blog, oneBanking App breaks down how both systems work and why SWIFT remains the banking world’s preferred option.
What SWIFT Actually Does (And Why It Dominates Global Banking)
SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) is not a system that moves money. It is a secure communication network that allows banks to send instructions to each other.
The SWIFT Code is an 8 or 11-character identifier helps banks verify:
- Which institution is sending the request
- Where the account is located
- What are the transfer instructions are
SWIFT matters because accuracy matters. One wrong digit in an international transfer can cause delays, failed transactions, or compliance issues. Banks trust SWIFT largely because:
- It has existed since 1973 and has continuously upgraded its security.
- It connects almost every major bank worldwide.
- It follows globally recognised financial rules and frameworks.
This long history gives SWIFT credibility and predictability, things banks value more than pure speed.
At oneBanking App, users frequently rely on SWIFT payment system Codes for accurate and secure transfers, which reinforces why banks continue depending on this system.
Where Blockchain Stands in Comparison?
Blockchain is not a messaging network. It is a decentralised ledger where transactions are recorded and confirmed directly on the network.
This means:
- No middlemen
- Faster settlement
- Transparent transaction history
And while public blockchains can settle transactions within seconds, not all banks can use public chains because of privacy, control, and regulatory demands.
Let’s compare both systems clearly:
| Feature | SWIFT | Blockchain |
| Function | Secure communication | Direct settlement |
| Speed | 1–3 business days | Seconds to minutes |
| Regulation | Fully recognised globally | Still unclear in many places |
| Users | 11,000+ institutions | Limited banking adoption |
| Reversibility | Possible through bank processes | Mostly irreversible |
Blockchain solves the speed challenge, but banking requires more than just speed. It requires trust, compliance, and accountability.
And for users, especially those relying on instant, low-friction payments through solutions like OneBanking App, the comparison only highlights how far traditional systems still need to go.
Why Banks Still Stay With SWIFT Over Blockchain?
Banking systems do not switch technologies just because something new appears. They evaluate risk, legality, operational cost, customer protection, and long-term stability. Here are the core reasons SWIFT still leads.

1. Clear Regulation and Compliance Frameworks
Every cross-border transaction must follow strict rules like:
- KYC (Know Your Customer)
- AML (Anti-Money Laundering)
- Sanctions screening
- Fraud detection
- Reporting requirements
The SWIFT payment system has built-in processes that help banks meet these rules. Blockchain does not yet have global regulatory clarity. Each country treats blockchain differently; some support it, some restrict it, and some are still figuring it out.
For banks, unclear regulation equals additional risk. That alone keeps blockchain from replacing SWIFT.
2. Universal Acceptance and Standardisation
A SWIFT Code works the same way in:
- India
- Germany
- Singapore
- UAE
- USA
This global standardisation is unmatched. Blockchain, on the other hand, has no single version. There are:
- Public blockchains
- Private blockchains
- Permissioned networks
- Consortium-based networks
Each comes with different rules and structures. Banks cannot rely on a system where every network works differently. SWIFT’s biggest strength is its uniformity.
3. Security With Accountability
SWIFT payment system messages are encrypted and follow well-tested security practices. When something goes wrong, like a failed instruction or incorrect messaging, there is a clear accountability trail. Banks know exactly:
- Who sent what
- When it was sent
- Which system processed it
- How to resolve the issue
Blockchain transactions, especially on public networks, are irreversible. Once funds move, they cannot be undone without additional arrangements. For banks dealing with large corporate clients and international settlements, this lack of reversibility creates hesitation.
4. Existing Banking Infrastructure Runs on SWIFT
Most banks built their core operational layers using the SWIFT system decades ago. That includes:
- Messaging infrastructure
- Compliance systems
- Reporting systems
- Fraud detection tools
- Internal settlement processes
Replacing the SWIFT payment system is not like replacing a software tool. It’s closer to rebuilding the engine of a running aircraft.
Switching to blockchain would require:
- New hardware
- New security checks
- Staff training
- Changes to regulatory approvals
- New reporting systems
- Rewriting entire operational workflows
The cost and time associated with this transition alone make large-scale blockchain adoption unrealistic for now.
5. Interoperability Across Countries and Banks
Every bank speaks SWIFT’s “language.” Blockchain does not have this comfort. Different networks cannot talk to each other without additional layers of technology.
Banks require simplicity: One global network → one set of rules → one standard.
SWIFT already offers this, which makes it the easiest and safest option. For platforms like oneBanking App that rely on regulated systems, SWIFT’s compliance structure makes international transfers predictable and safe.
Does That Mean Blockchain Isn’t Useful for Banks?
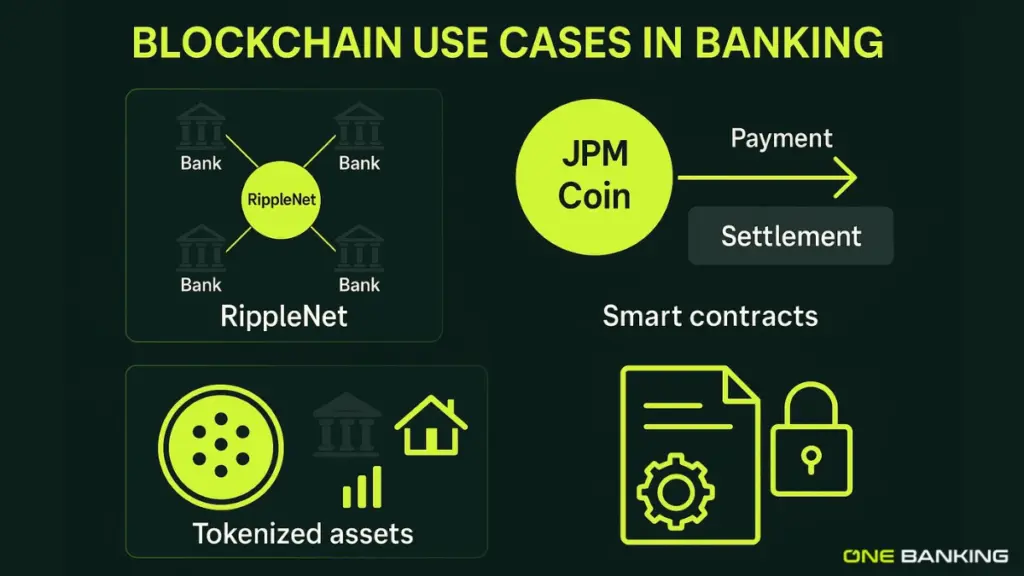
Not at all. Blockchain has become a strong alternative for specific use cases. Many global banks are experimenting with:
- Cross-border settlements
- Trade finance
- Tokenised assets
- Internal transfers
- Clearing between subsidiaries
Private blockchains like RippleNet, JPM Coin, and Onyx show that banks are already testing the technology in controlled environments. But these experiments are parallel systems, not replacements for SWIFT.
How SWIFT Is Evolving Too
SWIFT isn’t sitting still while blockchain evolves. It has introduced new upgrades such as:
SWIFT gpi (Global Payments Innovation)
- Faster cross-border transfers
- Real-time tracking
- Less waiting time for customers
- Better transparency
More than 4,000+ banks already use GPI because it reduces friction without changing the system completely.
ISO 20022 Standard
SWIFT is shifting to a richer messaging format that offers more data in each transaction, improving accuracy and compliance.
Work With Blockchain
SWIFT is actually exploring blockchain interoperability as well. The goal is not to compete with blockchain but to work alongside it.
Future: SWIFT + Blockchain Working Together
The future of global payments may not be either SWIFT or blockchain. It may be a hybrid model:
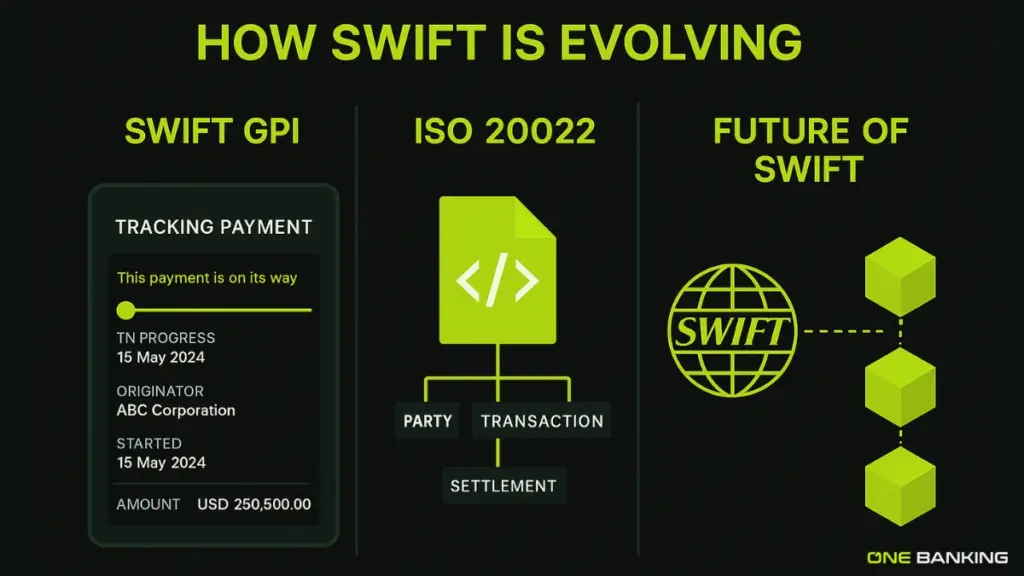
- SWIFT remains the global messaging backbone
- Blockchain handles faster settlement where required
- Banks use both, depending on the transaction type
Banks prefer reliability over disruption. So even as blockchain grows, SWIFT will continue to play a central role for years.
What This Means for Businesses and Customers
For most users, nothing changes directly. Whether a bank uses SWIFT or blockchain:
- Money reaches the destination
- The bank provides updates
- Security stays intact
- Compliance is ensured
But inside the banking system, SWIFT ensures consistency while blockchain introduces efficiency. The balance of both will shape the future payment environment.
Conclusion
SWIFT remains the backbone of global banking because it offers trust, regulation, consistency, and universal acceptance. Blockchain brings speed and innovation, but it still lacks standardised rules and clear regulatory frameworks. For now, the world’s financial system relies on SWIFT, and blockchain serves as a growing complementary technology.
At oneBanking App, we help users understand these systems so they can make smarter decisions when dealing with global payments.
FAQs:
SWIFT is a secure messaging system used by banks to send payment instructions. Blockchain directly settles transactions on a distributed ledger without intermediaries.
Banks use SWIFT because it is globally accepted, regulated, secure, and connects 11,000+ institutions. It provides standardised communication that meets strict compliance requirements.
Most banks avoid full blockchain adoption due to unclear regulations, privacy concerns, and high integration costs. Blockchain also lacks global standardisation compared to SWIFT.
Not at the moment. Blockchain is fast, but it doesn’t offer the compliance, acceptance, or accountability SWIFT provides.
SWIFT is not building its own blockchain, but it is testing ways to connect with blockchain networks. The goal is to improve interoperability, not replace its existing system.
No, banks play regulatory, legal, and compliance roles that blockchain networks cannot fully perform today.


Sumit
Nice one.